One-sixth of Indian plants have medicinal attributes but the threat of extinction looms large. The anti-fatigue property of Trichopus zeylanicustraditionally used by Kani tribes of Western Ghats in Kerala is an accepted fact discovered per chance by Council of Scientific and Industrial Research team during a forest expedition. Plant-derived compounds hold source of several clinically useful anti-cancer agents like vinblastine, vincristine and the chemical paclitaxel. Taking cognizance of healing properties of plants, this year AYUSH Ministry of the Government of India and the Department of Health & Human Services of the Government of USA along with National Institute of Health (US) and National Cancer Institute (US) conducted a workshop on fighting cancer with traditional medicine.

India has over 50,000 herbal formulations attributed under traditional knowledge falling under the ambit of Ayurveda, Unani, Siddha and Tibetan medicine and folk tradition. 960 medicinal aromatic plants are used by the contemporary trade and Ayurvedic industry and 178 species of them are consumed in volumes exceeding 100 metric tonnes per year and these constitute about 80% of the total industrial demand of all botanicals in the country. This dire need for medicines leads to rampant and over cultivation of plant parts leading to rare, endangered, critical and extinct state. It has been estimated by World Health Organization, WHO that 70 to 80 percent people worldwide resort to traditional, largely herbal medicine to meet their primary health-care needs. The global market potential is pegged at US$ 62 million but sadly India has less than 0.5% share. However, after China, India is the largest exporter of medicinal plants and herbal products. This is a result of export without proper certification that fetches low returns.
The Indian chapter of World Wildlife Fund TRAFFIC has deliberated over standards and certification schemes in medicinal and aromatic plants in India.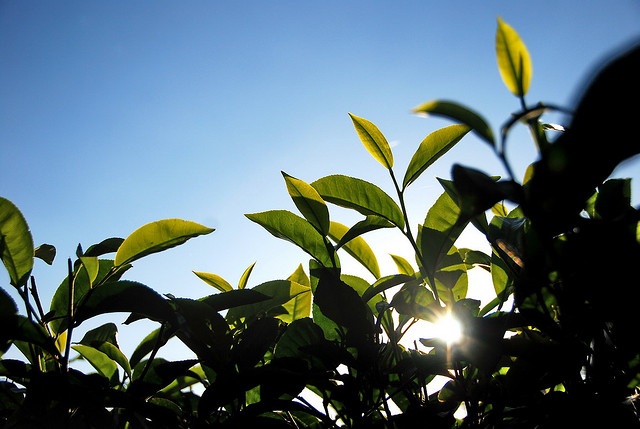

India has about 45,000 plant species and over a sixth of them standing at 7,333 are medicinal aromatic plants. But only 15% of medicinal plants are cultivated while the remaining 85% are collected by the industry from forest ecosystems and other natural habitats. Dr S K Niraj, spearheading TRAFFIC is apprehensive of the glaring threat of mass extinction of 3000 medicinal plants of India in the face of escalating commercial demand.
Dr M K Sarkar, former Additional Principal Chief Conservator of Forests, Tamil Nadu Forest Department has been working on bio-governance for endemic and threatened plants in India. According to Dr Sarkar ‘In the last 10 years, several Indian plants have gone extinct. It is estimated that more than 1200 plants that are exclusively found in India suffer from various degrees of threats. Again, 3471 species found in the Himalayas, 2015 species found in Peninsular India and 239 species in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands are under serious threats of extinction.’ The Biological Diversity Act, 2002 states that the Central Government is empowered to notify any species as threatened and make regulation on it. Forests being in the concurrent list, the central government can only give guidelines to the state. The state government has to make the implementation of their policies.
Dr. Sarkar corroborates, ‘Only 6 medicinal plants are covered under Indian Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 and remains so even after 44 years, till date. Wildlife Protection Act is stringent enough to protect animal species but covers only 6 plants. Forest Conservation Act of 1980 and 1988 harps only on habitat protection. Instead of negative listing and putting a ban on the use of these medicinal plants, they should be grown more and more. Banning leads to discouragement in the industry and less production and it gets more endangered owing to more illegal trade that can’t be stopped.’
‘70% of the medicinal plants are harvested in destructive way.’ asserts M.K.Ranjeet Singh, former forest secretary with Madhya Pradesh and also instrumental in framing of the India Wildlife Protection Act of 1972. Good Agricultural and Collection Practices for Medicinal Plants (GACP) are a set of guidelines developed by the World Health Organisation (WHO) aimed at improving the quality of medicinal plant material being used in the herbal medicines in the market. Dr S K Niraj, cautions, ‘If medicinal plants are not cultivated in a suitable environment, if they are harvested at the wrong time of the year or if they are processed incorrectly, the potency of the medical properties may be reduced, leading to the manufacture of ineffective herbal medicines’. Good Agricultural Practices (GAP) and Good Field Collection Practices (GFCP) lay down the main principles that should be followed by farmers and collectors to ensure they are producing medicinal plant materials with maximum levels of active ingredients.
Tribal population can derive thriving income from the cultivation of medicinal plants done on scientific lines to enable storage. The government has been offering them minimum support price to ensure tribal population to feel safe. S.S. Maity, deputy general manager with Tribal Cooperative Marketing Development Federation of India Ltd, under Ministry of Tribal Affairs says, ‘Around 35% of the income of tribal comes from medicinal plants. We have been teaching them ways of storage and processing into various items on scientific lines. TRIFED have been offering them minimum support price for 12 products.’
Ravi Singh, Secretary General and CEO with World Wildlife Federation, India points out, ‘India has just 22 certified medicinal plants whereas China has 200. I’ve spoken to people in Panna and Bundelkhand. They are unable to export medicinal plants owing to absence of certification.’ All medicinal plants exclusively found in India are teetering on extinction in the coming years if stringent contingency plan doesn’t get implemented.
The National Medicinal Plants Board (NMPB) under Ministry of AYUSH is implementing Central Sector Scheme, conservation of medicinal plants carried out mainly through in-situ conservation by way of plantation augmentation of species in their natural habitat and establishing Medicinal Plants Conservation and Development Areas (MPCDAs) through ex-situ conservation by developing herbal gardens.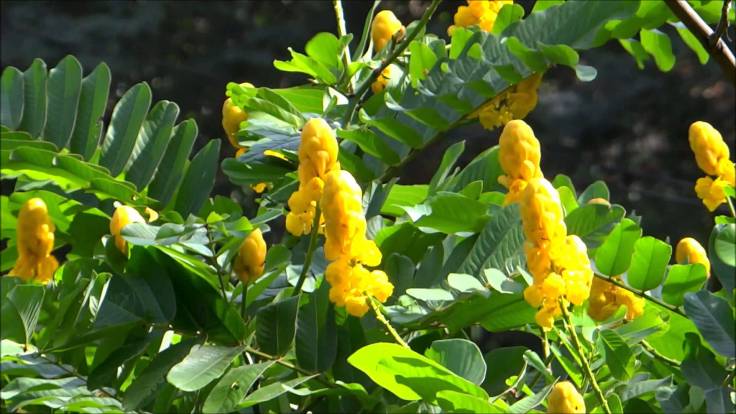

*The Author is a senior journalist and a radio documentary maker.
Some critically endangered species found only in India-
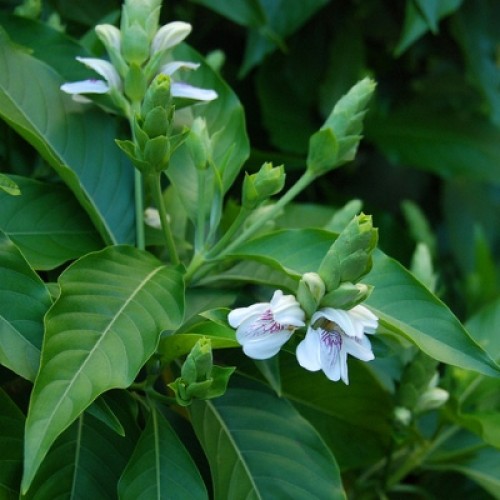
Picture 1.

Red sanders is highly endemic to Andhra Pradesh and extreme north areas of Tamil Nadu. Baba Ramdev’s Patanjali Yogpeeth in Haridwar purchased 706 metric tonnes of red sanders wood in a single government auction held last year. [Pic credit: Rawa Medherbs]
Picture 2.

Critically endangered Beddome’s cycas is endemic to Andhra Pradesh only is highly sought for Ayurvedic medicine. [Pic credit: Dr ABD Selvam, Botanical Survey of India]
Picture 3.
The Himalayan Yew occurs only in North East India, sought for Ayurveda and Tibetan medicine. [Pic credit: Dr ABD Selvam, Botanical Survey of India]
Picture 4.
Botanical Garden cum Recreational Park at Salaulim, Goa bordering Karnataka is located at the foothills of the Western Ghats along with the Salaulim Dam. It is flanked by Netravali Wildlife Sanctuary. This eco-trail of 33 kms from Madgaon is worth passes through idyllic hamlets and forests with excellent road conditions and very thin traffic. A full-fledged medicinal garden is coming up here











 Sambalan in Rajasthan and Samiksha in Odisha are good examples. Comprehensive school assessment framework called Shala Siddhi has been developed at the national level by NUEPA and launched in November 2016. This has a component of self-assessment and a third party assessment. The self -assessment will be used by schools to develop and implement their improvement plan.
Sambalan in Rajasthan and Samiksha in Odisha are good examples. Comprehensive school assessment framework called Shala Siddhi has been developed at the national level by NUEPA and launched in November 2016. This has a component of self-assessment and a third party assessment. The self -assessment will be used by schools to develop and implement their improvement plan.
